Organic Acids Test
We offer two types of tests; Lab Tests and Rapid Tests. This product is under the category Lab Tests. See all our Lab Tests by following the link.
See allWe offer several different options of testing methods. This test is done with Urine. See all tests done with Urine by following the link.
See allThe Organic Acids Test from GetTested is a detailed assessment measuring 21 different markers of the body’s metabolic processes. This test is ideal for uncovering the root causes of chronic illnesses and is particularly beneficial for individuals experiencing fatigue, burnout, or low energy. It is an easy to use test and therefore also suitable for children.
For those seeking further insights into their biochemical balance, we recommend the Neurotransmitters Basic Test, which measures levels of serotonin, dopamine, adrenaline, noradrenaline, and the ratio between adrenaline and noradrenaline.
- In stock
- At-home tests
- Fast delivery

Get 5% off on 2 Lab tests, and 10% off on 3 Lab tests or more.
About the Organic Acids Test
The Organic Acids Test measures a broad group of substances used in the body’s basic metabolic processes. When you analyse organic acids, you gain insight into how your body uses nutrients from food and converts them into energy (ATP). This process involves enzymes and their cofactors. If you lack these cofactors or if the enzymes are not working optimally, certain substances may accumulate. Measuring these substances’ concentrations can reveal potential vitamin and mineral deficiencies. Additionally, metabolic products of neurotransmitters in urine can indicate stress hormone imbalances, and dysbiosis markers may point to bacterial imbalances in the gut.
Indicators measured by the test
Items measured for Lipid metabolism
Carbohydrate metabolism
Organic acids in the citric acid cycle
Organic acids of vitamin metabolism
Degradation of neurotransmitters
Dysbiosis markers
The health benefits of Organic Acids
Organic Acids have various health benefits such as:
- Maintaining the cellular integrity of the gut lining
- Improving digestion
- Reducing inflammation
- Improving the absorption of proteins, amino acids and minerals.
- Protecting the immune system by providing energy and regulating metabolism
It is important to have a decent amount of Organic Acids in the body, not too little but also not too much, as too many Organic Acids can cause side effects like nausea, vomiting or diarrhoea. Consult with your healthcare provider about whether you should take supplements or make dietary changes after receiving your Organic Acid test results.
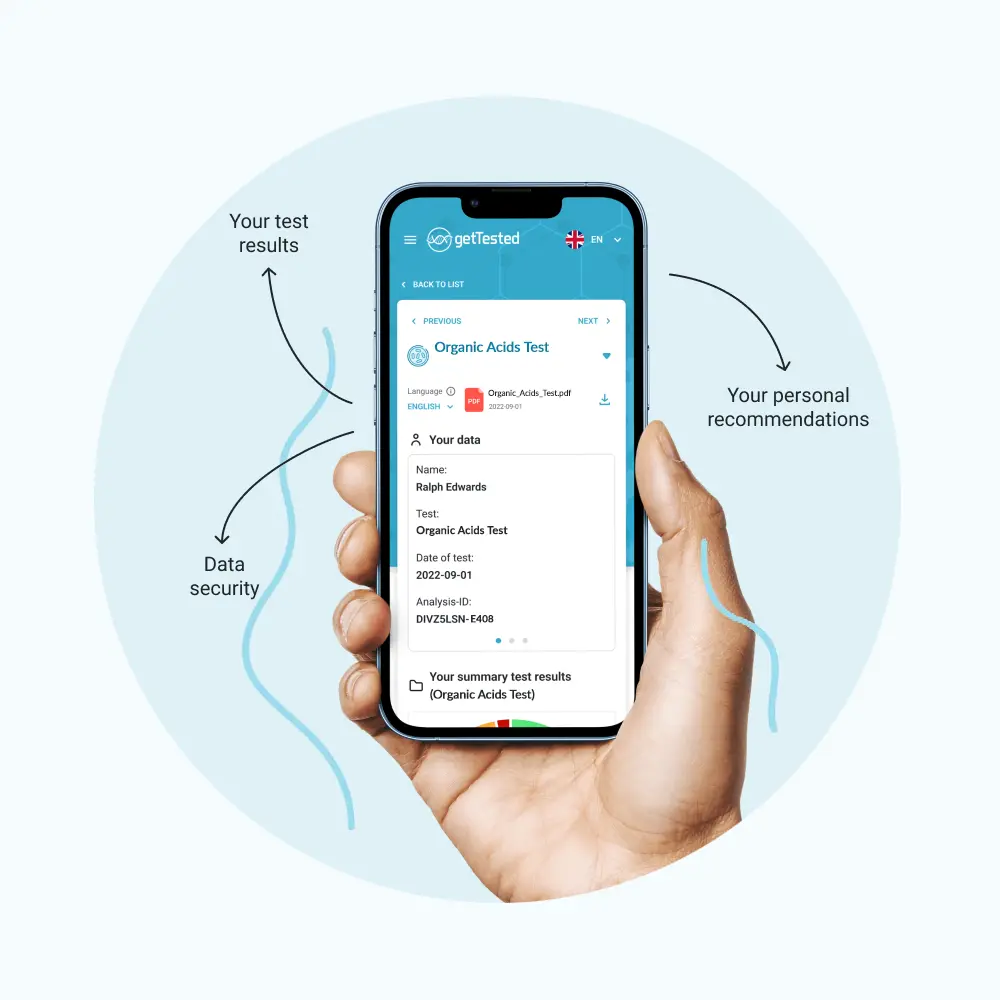
Understanding Your Health with our test
GetTested is dedicated to offering accessible and accurate health diagnostics. We designed our Organic Acids test to empower you with knowledge about your health status. The urine organic acids test is a convenient test, because you can simply collect a urine sample from the comfort of your home using our user-friendly test kit.
Urine testing is highly effective, because organic acids are found in high amounts in urine. The special lab techniques separate the acids out to analyse them. If you may have a metabolic imbalance, it may show up as abnormal organic acids in your test results.
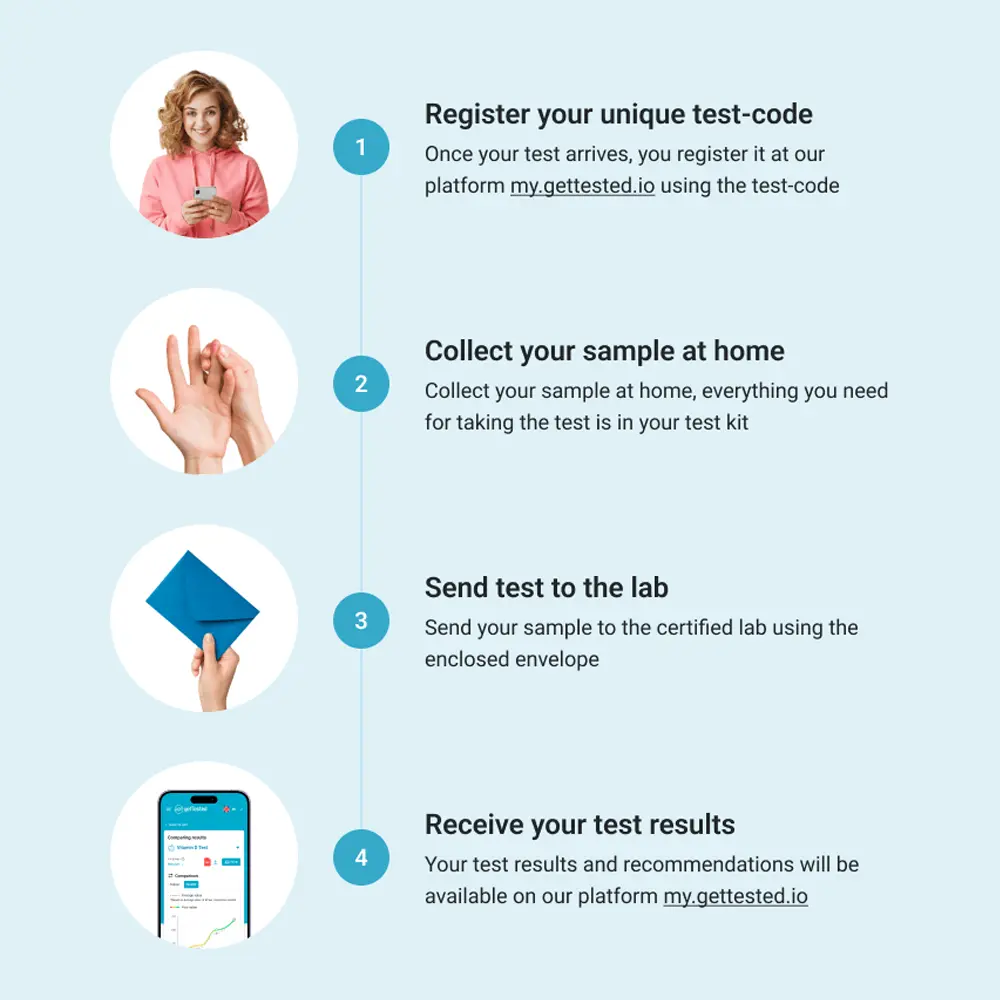
How to perform the Organic Acids Test
You perform the Organic Acids Test at home by collecting your second morning urine. After collecting the sample, you send it to a lab for analysis. You will receive your digital test results once the lab completes the analysis. Since the Organic Acid Test uses a urine sample, it is suitable for children as well.
FAQ
How is the Organic acids test carried out?
When should I take the test?
How quickly will I receive my results?
What does urine organic acids test for?
What does organic acids test show?
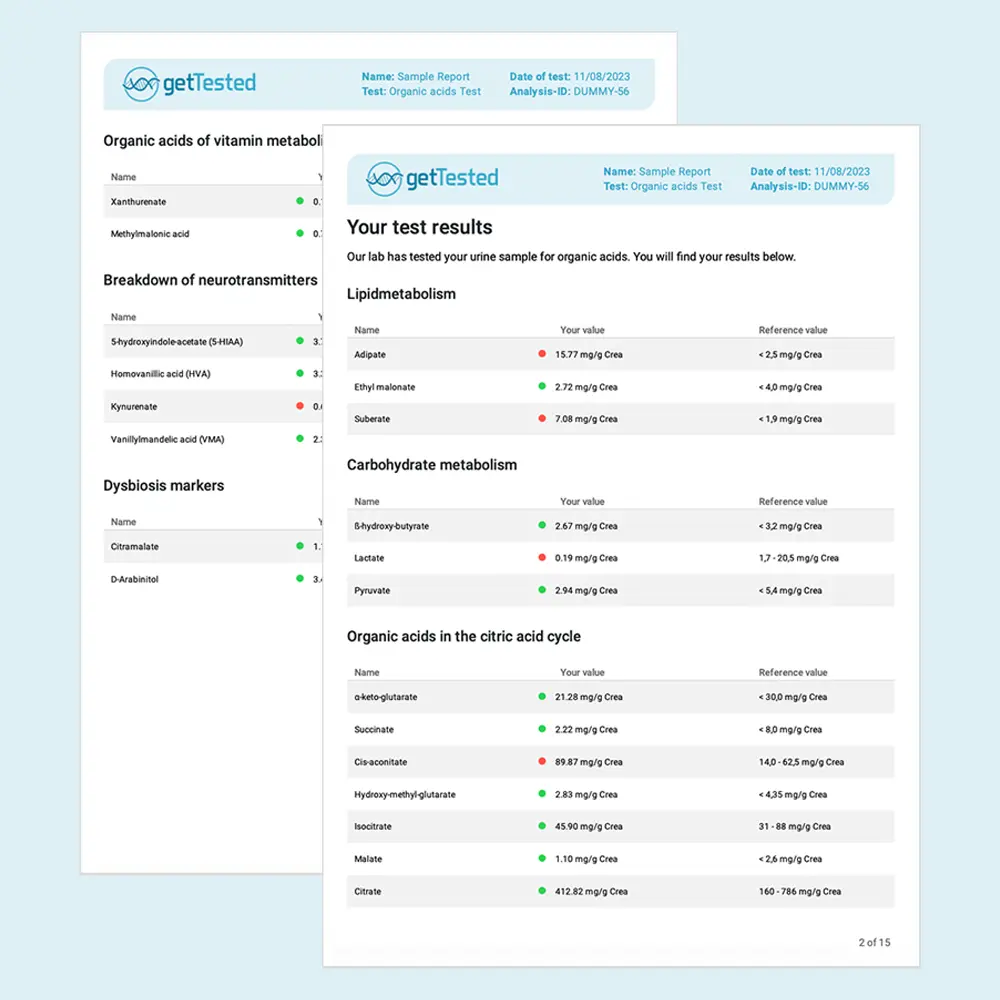
Example Report
Example of Organic Acids Test
Reviews
-
Revelatory insights. Comprehensive report. Improved my health strategy immensely.
-
informative and insightful
Related Products
-
Candida Test
GetTested's Candida Test is designed for individuals suspecting an overgrowth of the ...€ 59,00 Add to cart -
Gut Microbiome Test XL
The Gut Microbiome Test XL is for those who really want to understand their health. W...€ 289,00 Add to cart -
Heavy Metals Test
Heavy metals are among the most significant health concerns of our time. They can gen...€ 149,00 Add to cart -
Neurotransmitters Basic
Neurotransmitters play a crucial role in shaping our behavior and emotions. Imbalance...€ 159,00 Add to cart -
Vitamin Test Total (Deficiency Test)
The Vitamin Test Total by GetTested provides an opportunity to understand one's vitam...Original price was: € 283,00.€ 267,00Current price is: € 267,00. Add to cart
You may also like…
Trusted by over 10.000+ customers


“The home test was straightforward with easy to follow instructions. The test result was detailed and clear in its presentation. Also had the opport...”
Richard

“We looked at a lot of companies offering the same services but made the decision to go forward with get tested because the labs are based here in t...”
Natasha

“There are other providers out there, I have tried 3. Gettested was the fastest and the customer service was the best. I even received my test on th...”
Alan

“Absolutely perfect, results came after few days and finally after a lots of times visited GP, we finally know why my son has eczema - he is allergy...”
E

“I found them to be professional and not too long a wait for results. Helpful with any after questions. Will be using them again if need be. I highl...”
Eileen

“I really value my test and to see the results. It is a jungle when your health is online. So get accurate and precise knowledge is a gift, as it is...”


























Leave a Reply